
Introduction to Cloud Analytics and Big Data
Today, businesses rely heavily on cloud computing and big data to stay competitive. Cloud computing has transformed data storage, processing, and analysis, while big data tools allow companies to gain insights from various data types. Using these technologies effectively is key for businesses to innovate, make better decisions, and increase profits.
What is Cloud Analytics?
Cloud analytics is using cloud platforms to analyze data. It allows companies to process and analyze big data without buying expensive hardware and infrastructure. The cloud makes it easier and cheaper to do data analysis at a large scale.
What are the benefits of cloud-based analytics?
Cloud-based analytics solutions offer numerous benefits, including faster time-to-insights, easier collaboration among teams, and the ability to quickly scale resources up or down based on changing needs. For example, the clothing retailer ASOS uses Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics to process and analyze billions of customer interactions and transactions, enabling real-time personalization and product recommendations. Azure Synapse Analytics combines big data analytics, data warehousing, and data integration into a single, unified platform, allowing ASOS to query both relational and non-relational data at petabyte scale with unmatched performance.
The Power of Big Data
Big data refers to the massive, complex datasets that are generated by businesses, governments, and individuals every day. The scale of big data is staggering, with billions of gigabytes of data generated every day.
Many cloud service providers offer big data storage and processing solutions designed to handle these massive volumes of data, providing scalable, distributed repositories that can store trillions of files and petabytes of data in their native format. These solutions often integrate seamlessly with other big data services, allowing organizations to build end-to-end big data analytics solutions in the cloud.
Effectively harnessing big data requires specialized technologies, such as distributed storage and processing systems, as well as advanced analytics techniques like machine learning and data mining.
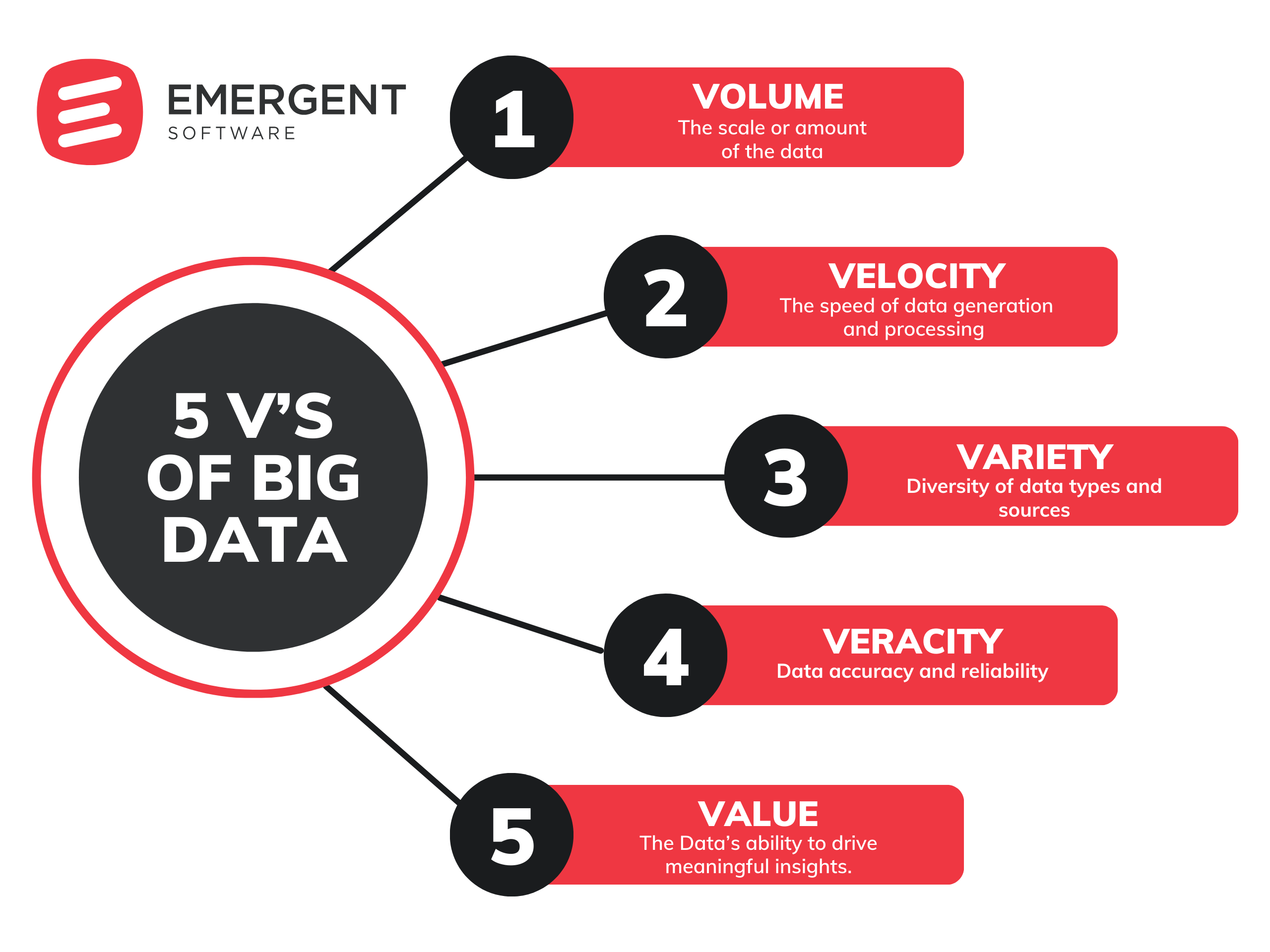
The 5 V’s of Big Data
Big data has become a critical asset for organizations seeking to gain a competitive edge. To effectively leverage big data, it's essential to understand its defining characteristics, commonly known as the "5 V's." These characteristics provide a framework for assessing the challenges and opportunities associated with big data initiatives. By considering volume, velocity, variety, veracity, and value, organizations can develop strategies to take advantage of the power of their data and drive meaningful insights.
Big data datasets are characterized by the "5 V's":
- Volume: the scale or amount of the data
- Velocity: the speed of data generation and processing
- Variety: diversity of data types and sources
- Veracity: data accuracy and reliability
- Value: the data’s ability to drive meaningful insights
The Synergy of Cloud Computing and Big Data
The combination of cloud computing and big data is a powerful one. The cloud provides the scalable, on-demand infrastructure necessary to store and process huge volumes of data, while big data technologies enable organizations to analyze and derive insights from that data in near real-time.
By leveraging the cloud, companies can easily scale their big data workloads up or down as needed, without worrying about managing complex on-premises infrastructure. This flexibility is especially valuable in today's rapidly changing business landscape, where agility and adaptability are key to success.
Many cloud providers offer auto-scaling capabilities that ensure resources are automatically provisioned or deprovisioned based on workload demands, optimizing performance and cost-efficiency.
Driving Data-Informed Decision Making
One of the most significant advantages of combining cloud analytics with big data is the ability to make more informed, data-driven decisions. By analyzing large, diverse datasets, organizations can uncover hidden patterns, correlations, and insights that would be impossible to discern manually.
This data-driven approach can lead to significant improvements in various aspects of business operations, including inventory management, customer engagement, and overall satisfaction.
Many cloud service providers offer cognitive services and machine learning APIs that enable developers to easily integrate intelligent features like sentiment analysis, computer vision, and natural language processing into their applications, empowering organizations to gain deeper insights from their big data.
Ensuring Data Quality and Governance
To truly maximize the value of cloud analytics and big data, organizations must prioritize data quality and governance. Inaccurate, inconsistent, or incomplete data can lead to flawed analyses and poor decision-making.
Implementing robust data governance policies, such as standardized data formats, metadata management, and data lineage tracking, can help ensure the accuracy and reliability of data assets. Regular data quality audits and cleansing processes are also essential to maintain the integrity of data over time.
Choosing the Right Tools and Platforms
With the proliferation of cloud analytics and big data technologies, choosing the right tools and platforms for your organization can be a daunting task. It's important to carefully evaluate the capabilities, costs, and ease-of-use of different solutions to find the best fit for your specific needs.
Microsoft Azure offers a comprehensive set of cloud analytics and big data services, including Azure Synapse Analytics, Azure Databricks, Azure HDInsight, and Azure Data Factory, each designed to address different aspects of the big data lifecycle.
For instance, the National Basketball Association (NBA) uses Azure Databricks to process and analyze over 50 terabytes of game data, including player tracking data, video feeds, and fan sentiment data from social media. By leveraging Azure Databricks' fast and collaborative Apache Spark-based analytics platform, the NBA can generate real-time insights and predictions, such as identifying the most effective player lineups and optimizing ticket pricing based on demand forecasts.
Compliance and Regulatory Challenges
As organizations increasingly rely on cloud-based analytics and big data, they must also navigate a complex and evolving regulatory landscape. Data privacy and protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and similar regulations in other jurisdictions, place strict requirements on how personal data can be collected, stored, and used.
Ensuring compliance with these regulations is critical to avoiding costly fines and reputational damage. Organizations must work closely with their cloud providers and legal teams to implement appropriate data protection safeguards and maintain transparency around their data practices. Many cloud service providers offer a comprehensive set of compliance offerings, including numerous certifications and attestations, such as ISO 27001, HIPAA, and FedRAMP, helping customers meet their regulatory obligations.
Addressing the Skills Gap
Another significant challenge in maximizing the value of cloud analytics and big data is the skills gap. As these technologies continue to evolve at a rapid pace, many organizations struggle to find and retain talent with the necessary skill sets. Data scientists, cloud architects, and big data engineers are in high demand, and competition for these roles can be fierce. To overcome this challenge, companies must develop creative strategies for attracting and retaining top talent, such as offering competitive compensation packages, providing opportunities for continuous learning and development, and fostering a culture of innovation and experimentation.
Emerging Technologies and Future Trends
As cloud analytics and big data continue to evolve, several emerging technologies are poised to reshape the landscape. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are increasingly being integrated into cloud analytics platforms, enabling more advanced and automated data analysis capabilities.
Many cloud service providers offer a wide range of AI and machine learning services, empowering organizations to infuse intelligent capabilities into their applications and analytics workflows. For example, hospitals can use machine learning to predict and prevent patient readmissions, improving outcomes and reducing costs. By analyzing electronic health records, lab results, and demographic data, hospitals can identify high-risk patients and intervene early with personalized care plans and follow-up services.
Edge computing, which involves processing data closer to the source rather than in centralized cloud data centers, is also gaining traction as a way to reduce latency and bandwidth costs for IoT and real-time analytics applications.
Many cloud providers offer managed services that enable organizations to deploy cloud workloads and analytics capabilities directly on IoT devices, enabling real-time insights and actions at the edge. For instance, energy management and automation companies can use edge computing to optimize their manufacturing processes and improve energy efficiency. By deploying machine learning models and analytics algorithms directly on industrial equipment, these companies can make real-time decisions based on sensor data, reducing energy consumption and maintenance costs.
New Business Models and Service Offerings
The rise of cloud analytics and big data is also giving rise to new business models and service offerings. Data as a Service (DaaS), for example, enables companies to monetize their data assets by providing access to curated datasets via API or subscription models. Many cloud service providers offer fully managed services that allow organizations to securely share big data with external partners and customers, enabling new data monetization opportunities and collaborative analytics scenarios.
Leading providers of business data and analytics can use these services to securely share their commercial datasets with customers and partners, enabling them to enrich their own data and gain deeper insights into market trends and customer behavior.
Predictive and prescriptive analytics, which use machine learning algorithms to forecast future trends and recommend optimal actions, are also becoming increasingly popular as organizations seek to stay ahead of the curve. Many cloud providers offer cognitive services that enable organizations to easily integrate predictive and prescriptive analytics capabilities into their applications, driving more proactive and optimized decision making. For example, aerospace companies can use anomaly detection services to identify potential quality issues in their aircraft manufacturing processes, reducing defects and improving safety.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
In conclusion, maximizing the value of cloud analytics and big data is a critical imperative for modern businesses looking to stay competitive in an increasingly data-driven world. By leveraging the scalability and flexibility of cloud computing platforms, and harnessing the power of advanced big data and analytics services, organizations can gain deeper insights, make better decisions, and drive meaningful business outcomes. However, realizing this value requires a strategic approach that encompasses data quality and governance, the right tools and platforms, a data-driven culture, and the ability to navigate complex challenges like regulatory compliance and talent acquisition. Studies estimate that big data could unlock hundreds of billions to trillions of dollars in economic value across various industries in the coming years, underscoring the immense potential of these technologies.
As the technology landscape continues to evolve, with new innovations like AI, edge computing, and DaaS on the horizon, the opportunities for businesses to leverage cloud analytics and big data will only continue to grow. Companies that can effectively leverage these technologies and build a truly data-driven organization will be well-positioned for success in the years to come. The time to invest in your cloud analytics and big data capabilities is now - the future belongs to those who can turn data into a strategic asset and competitive advantage. By embracing the transformative potential of cloud computing and committing to data-driven excellence, organizations can unlock new sources of value, drive innovation, and chart a course for long-term growth and success.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do you maximize data analytics?
Maximizing data analytics involves leveraging the scalable and flexible infrastructure of cloud computing to handle large volumes of data efficiently. Ensuring data quality through rigorous data management practices and selecting appropriate analytics tools that align with organizational goals are key. Building a data-driven culture that promotes collaboration across teams and addressing regulatory compliance and talent acquisition challenges further enhances the effectiveness of data analytics initiatives.
2. What are the benefits of performing big data analytics in the cloud?
Performing big data analytics in the cloud offers several advantages, including scalability to handle vast amounts of data, flexibility to adapt resources based on fluctuating demands, and cost-efficiency by eliminating the need for extensive on-premises infrastructure. Cloud environments facilitate faster time-to-insights through parallel processing capabilities and enable easier collaboration across geographically dispersed teams, enhancing overall operational efficiency and agility.
3. What is the role of cloud computing in big data analytics?
Cloud computing plays a crucial role in big data analytics by providing the scalable, on-demand infrastructure necessary to store, process, and analyze massive datasets in real-time. Cloud platforms offer a wide range of services and tools specifically designed for big data applications, such as distributed computing frameworks and managed data services, enabling organizations to derive valuable insights from their data with enhanced speed and efficiency.
4. What is big data analytics in cloud computing?
Big data analytics in cloud computing refers to the practice of analyzing large and complex datasets using cloud-based infrastructure and services. It involves leveraging cloud resources to process and derive actionable insights from diverse data sources, such as structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. This approach allows organizations to harness the scalability, computational power, and cost-effectiveness of cloud platforms to perform advanced analytics tasks that were traditionally challenging to execute with on-premises systems.
5. What is the difference between cloud data and big data?
Cloud data refers to any data stored or processed in cloud environments, regardless of its volume or complexity. It encompasses all types of data managed within cloud platforms, including operational data, user-generated content, and structured databases. On the other hand, big data specifically refers to datasets characterized by their massive volume, high velocity, and diverse variety, which often require specialized tools and techniques for storage, processing, and analysis. While cloud data can include big data, not all cloud data is necessarily big data.
6. What is the difference between cloud analytics and data analytics?
Cloud analytics refers to the use of cloud-based tools and platforms to perform data analytics tasks, leveraging the scalability and flexibility of cloud computing environments. It involves utilizing cloud resources for data storage, processing, and analysis, often incorporating advanced analytics techniques like machine learning and predictive modeling. In contrast, data analytics is a broader term that encompasses the entire process of examining data to uncover insights, irrespective of where the data resides—whether in the cloud, on-premises, or in hybrid environments.






